A human-centred approach is a key to the success of the digital transformation.

Services
WHY IS IT IMPORTANT TO THINK DIFFERENTLY?
The application of the principles of human orientation and ergonomics in the processes of design and development of information systems creates significant social and economic benefits for the employees of organisation, clients and related interest groups. Exceptionally easy-to-use systems and products are more successful both technically and operationally. If users understand how to use the system without external assistance, the organisation has a lower burden of system servicing, and fewer queries and complaints are raised. In certain cases where a user has several alternative methods to achieve the objective, user-friendliness is an essential factor determining the choice of using an information system, service or product.
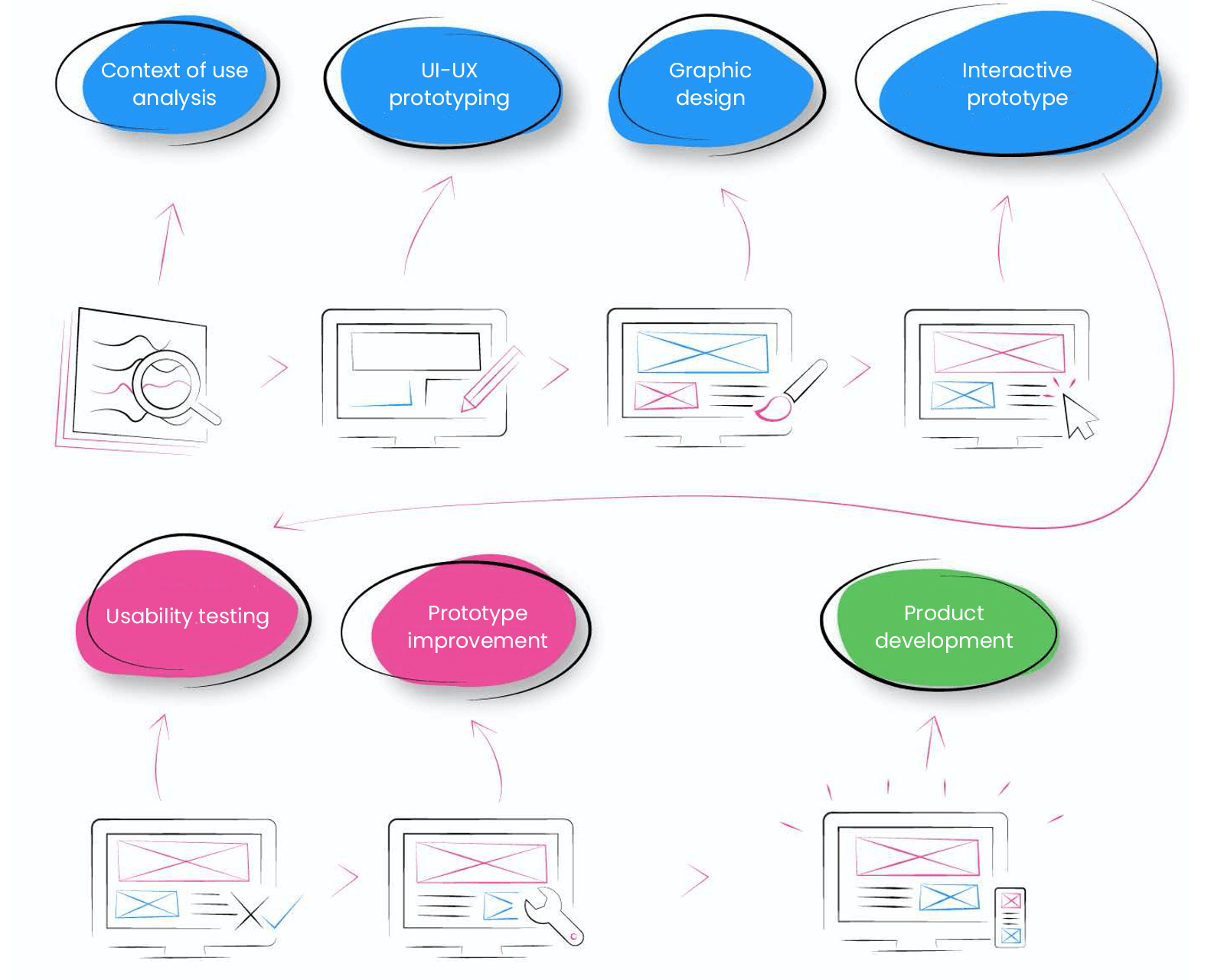
Designing human-centred systems
In the development of a new solution, we use a prototyping production model. The project is divided into two stages: (a) the development of a prototype and (b) the marketing of the product. Significant attention is paid to the creation of a prototype, during which time the analysis of needs is carried out, and surveys of interested people and discussions with end users are organised. A number of options for implementing the solution are developed: a solution model, prototype and designs from which the best option by means of surveys/discussions is selected. A solution model is developed on the basis of the chosen concept and tested with a target group of users. The design model is improved on the basis of the results of the tests and submitted for reassessment. In this way, the testing–improvement cycles of the design model can be repeated until the result is confirmed as meeting user expectations and objectives. Once the model is approved, the marketing stage of the product may be commenced.
Services
- Activity analysis and development of the product concept;
- Preparation of technical architecture;
- Design of the user interface and preparation of the prototype for testing;
- User interface design;
- Product prototype testing with users;
- Preparation of detailed project implementation requirements.
Software development
Through the combination of best engineering practices, we can promptly deliver a high-quality product, meet the customer’s business needs to the maximum and fulfil the expectations of end users. In the system production process, we apply the Agile Scrum model philosophy, which is based on strict discipline, transparency and accountability of the project management process, self-regulation and decision-making freedom given to the initiator.
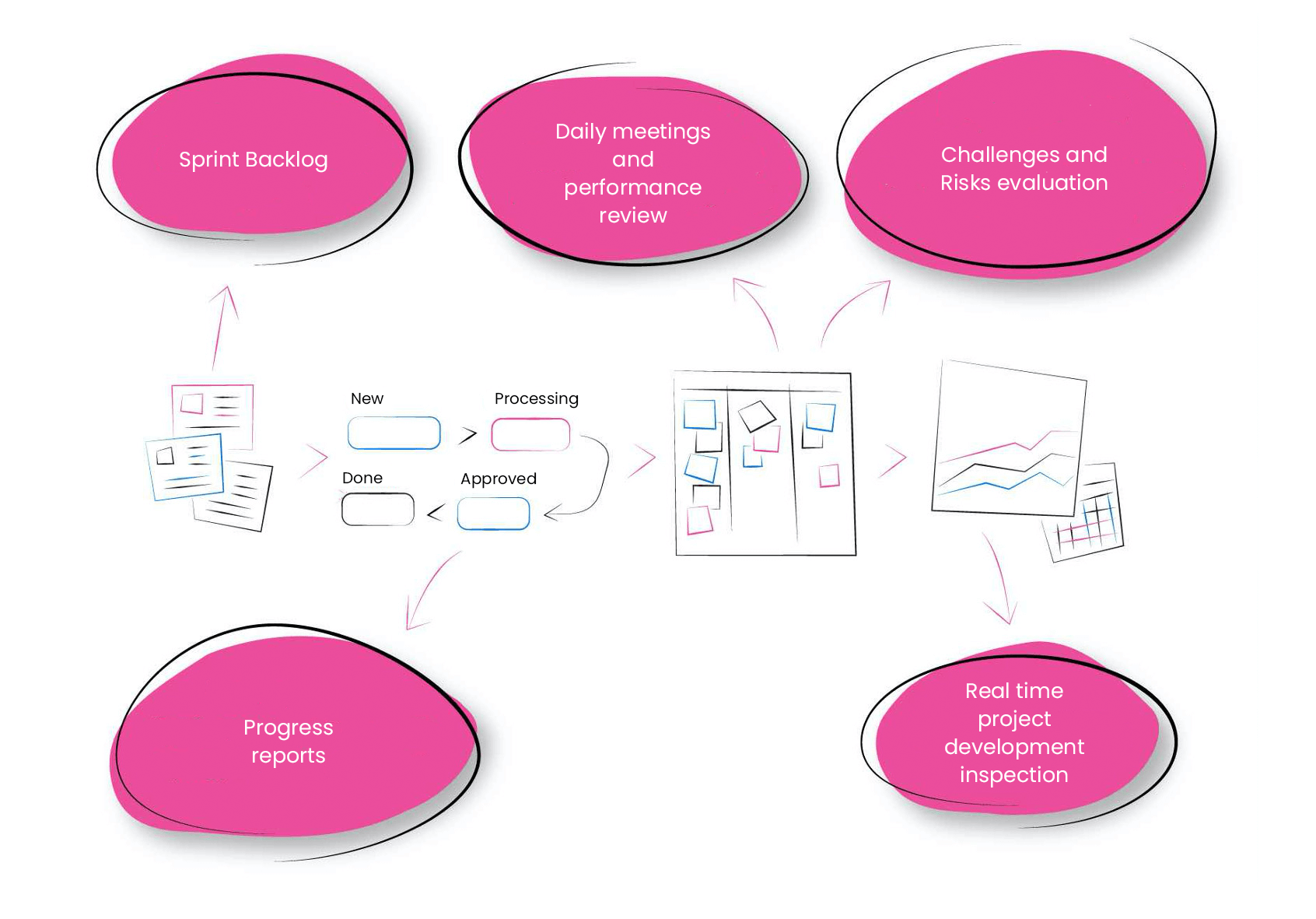
Applying an iterative-incremental Agile Scrum model, the software is developed in cycles called sprints, which last 2–3 weeks. Closely cooperating teams (4–6 people) work on the project. The method is usually combined with extreme programming, which ensures that programmers can exchange tasks or mobilise resources to solve critical tasks. The solution created at the end of each cycle is verified, tested and presented to the customer. This is reviewed, comments are submitted and new requirements for further product development and priorities of activity are formulated. At the end of the stage (sprint), time is devoted to discussing problems and lessons learned, which ensures continuous improvement of implementation efficiency and teamwork productivity.
SERVICES
- Software development by Internet technology (PHP);
- Development of mobile apps (iOS, Android);
- Installation of databases (MariaDB, SQL, Oracle);
- Implementation of the user interface (Angular, Javascript, HTML/CSS);
- Integration with external and internal information systems (XML);
- Accessibility for the disabled;
- Search engine optimisation (SEO).
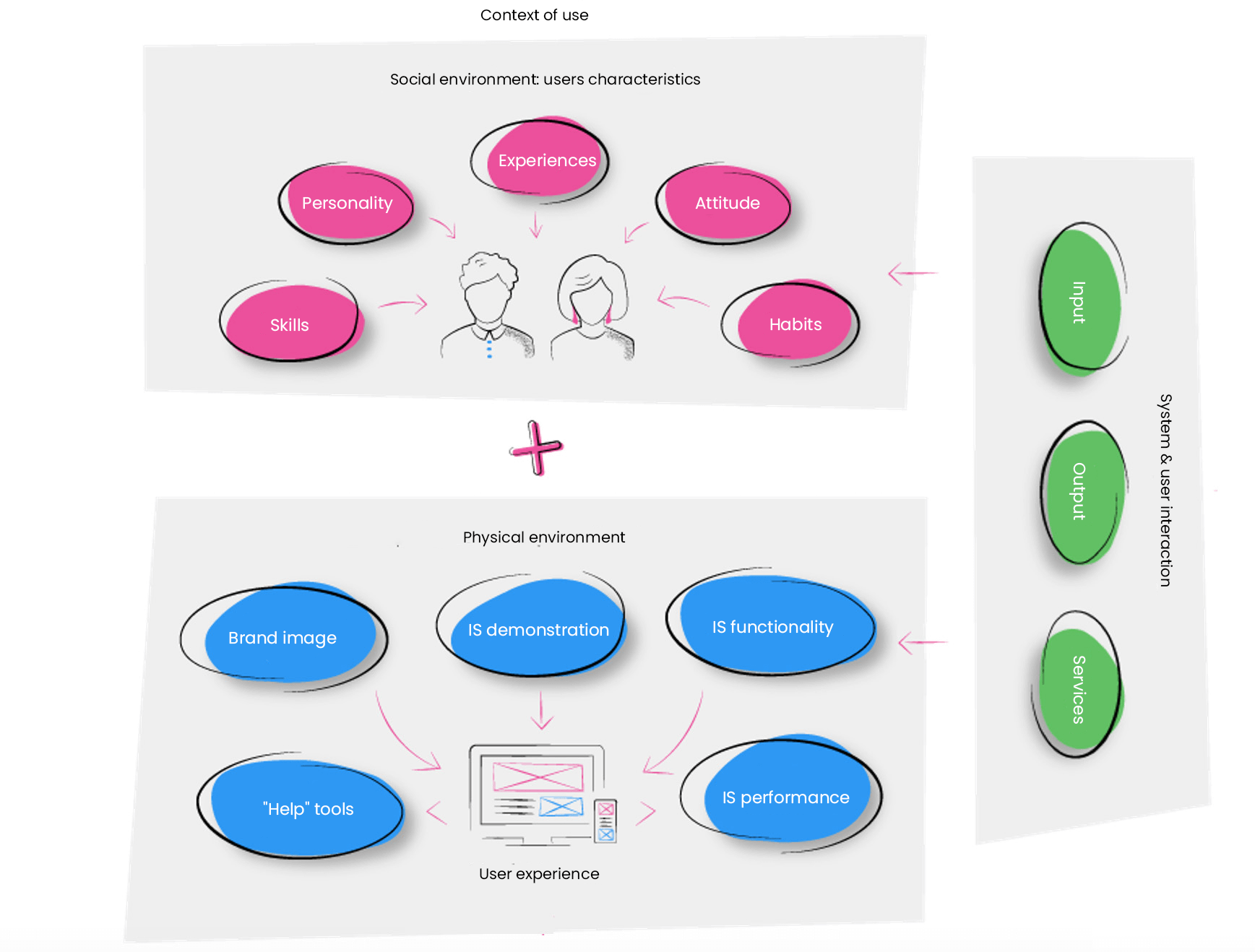
Assessment of system ergonomics and user experience
With a view to creating a human-centred system, it is necessary to assess the product being developed from a user perspective. The assessment being carried out in the early stages of the project allows identification of the additional needs of users, learning about the advantages and disadvantages of the created product, assessing whether expectations of the users are met, comparing alternative navigation, design and functional solutions, and selecting the most appropriate ones.
SERVICES
- Expert assessment of system user-friendliness;
- User experience testing (heatmaps);
- Assessment of user satisfaction;
- User and usability testing;
- Card sorting;
- Sitemap testing.